geom_hourglass() takes a continuous datetime object, splits in in discrete dates and
time of day with stat_hourglass(). This geometry is a wrapper
to add it as a layer to a ggplot. GeomHourglass is a ggproto object inheriting from
?ggplot2::GeomPoint. It should not be used directly. Instead call geom_hourglass().
Usage
GeomHourglass
geom_hourglass(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
stat = "hourglass",
position = "identity",
na.rm = FALSE,
show.legend = NA,
hour_center = 0,
inherit.aes = TRUE,
...
)Arguments
- mapping
Set of aesthetic mappings created by
ggplot2::aes(). If specified andinherit.aes = TRUE(the default), it is combined with the default mapping at the top level of the plot. You must supply mapping if there is no plot mapping. Thehourglassstatandgeomrequires either thexaxis or theyaxis to be mapped. The mapped aesthetic will show the date of the variable, whereas the opposite axis will show the time of day.- data
The data to be displayed in this layer. If
NULL, the default, the data is inherited from the plot data as specified in the call toggplot2::ggplot(). Otherwise, adata.frame, or other object, will override the plot data. All objects will be fortified to produce a data frame. Seeggplot2::fortify()for which variables will be created. The data should contain a column with datetime values (e.g.,?POSIXct)- stat
Can be used to overwrite the default connection between
geom_hourglassandstat_hourglass().- position
A position adjustment to use on the data for this layer. This can be used in various ways, including to prevent overplotting and improving the display. The
positionargument accepts the following:The result of calling a position function, such as
position_jitter(). This method allows for passing extra arguments to the position.A string naming the position adjustment. To give the position as a string, strip the function name of the
position_prefix. For example, to useposition_jitter(), give the position as"jitter".For more information and other ways to specify the position, see the layer position documentation.
- na.rm
If
FALSE, the default, missing values are removed with a warning. IfTRUE, missing values are silently removed.- show.legend
logical. Should this layer be included in the legends?
NA, the default, includes if any aesthetics are mapped.FALSEnever includes, andTRUEalways includes. It can also be a named logical vector to finely select the aesthetics to display.- hour_center
The hour at which the time of day is centred. Default is 0, meaning midnight. -12 centres around noon of the preceding day, +12 centres around noon of the next day.
- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics, rather than combining with them. This is most useful for helper functions that define both data and aesthetics and shouldn't inherit behaviour from the default plot specification, e.g.borders().- ...
Arguments passed to geometry.
Value
Returns a ggplot2::layer() which can be added to a ggplot2::ggplot()
Examples
library(ggplot2)
data(bats)
monitoring <- attr(bats, "monitoring")
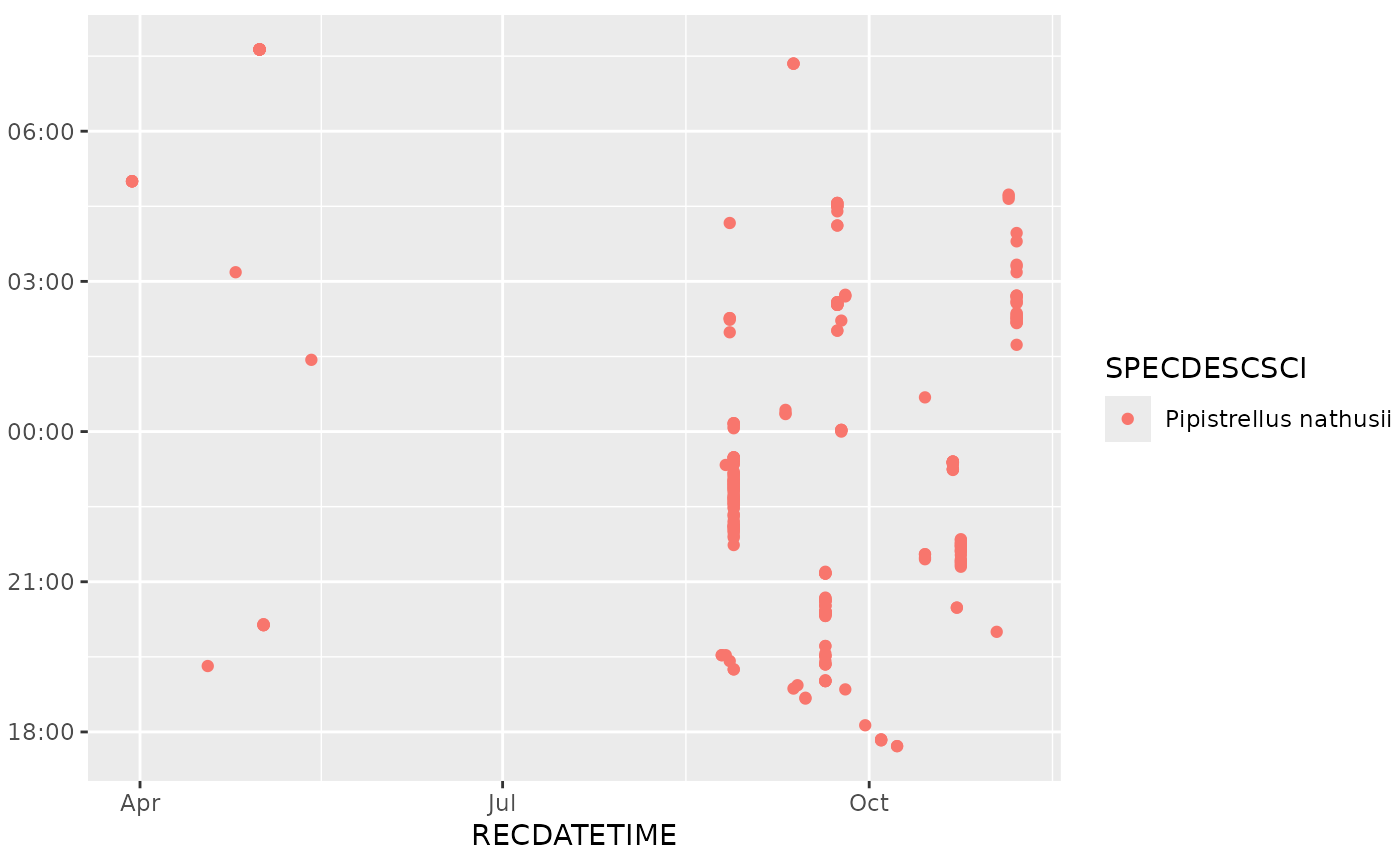
ggplot(subset(bats, format(RECDATETIME, "%Y") == "2019"),
aes(x = RECDATETIME, col = SPECDESCSCI)) +
geom_hourglass()
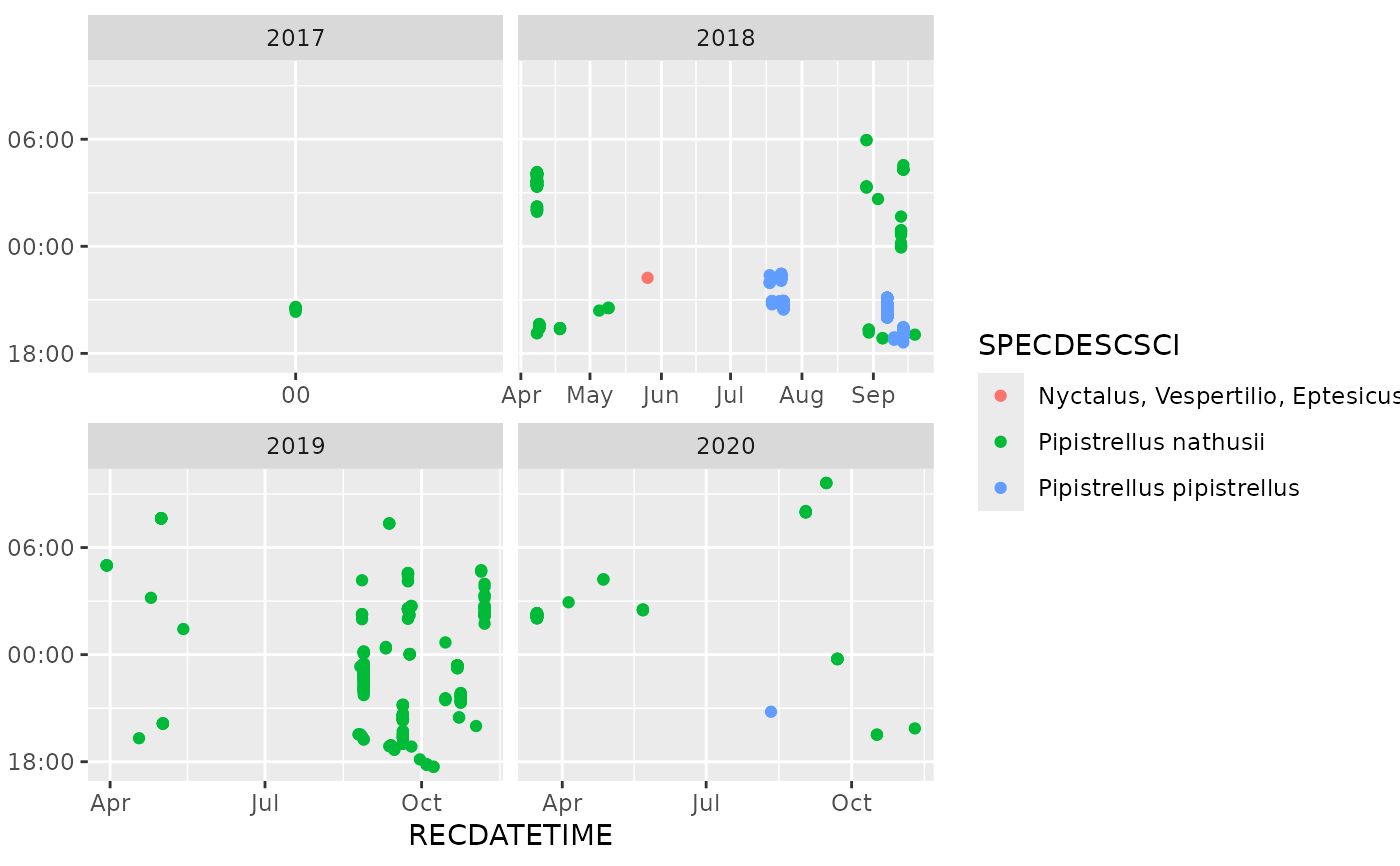
 ggplot(dplyr::mutate(bats, YEAR = format(RECDATETIME, "%Y")),
aes(x = RECDATETIME, col = SPECDESCSCI)) +
geom_hourglass() +
facet_wrap(~YEAR, scales = "free_x")
ggplot(dplyr::mutate(bats, YEAR = format(RECDATETIME, "%Y")),
aes(x = RECDATETIME, col = SPECDESCSCI)) +
geom_hourglass() +
facet_wrap(~YEAR, scales = "free_x")